A Deadly Virus Threat: The Eastern Equine Encephalitis Virus in Massachusetts
Massachusetts has been grappling with a significant public health threat posed by the Eastern Equine Encephalitis (EEE) virus. This mosquito-borne illness can be fatal to both humans and horses, making it a serious concern for residents and visitors alike. In this article, we will delve into the details of EEE, including its causes, symptoms, precautions, and the areas currently affected in Massachusetts.
Understanding EEE
Eastern Equine Encephalitis (EEE) is a rare but potentially fatal viral disease transmitted through the bite of infected mosquitoes. The virus primarily affects horses, but it can also infect humans. While human cases are relatively uncommon, the mortality rate for EEE is alarmingly high, reaching up to 33% in those who develop severe illness.
A History of EEE in Massachusetts
Massachusetts has seen several EEE outbreaks over the years, with notable surges in cases during the late summer and early fall. The state has responded with various public health initiatives, including aerial mosquito spraying and community awareness campaigns. The 2019 outbreak, for instance, resulted in 12 human cases and 6 fatalities, prompting widespread concern and intensified efforts to control the mosquito population. Understanding the history of EEE in the state highlights the ongoing challenge of managing this deadly virus.

Causes and Transmission
The EEE virus is primarily transmitted by mosquitoes, specifically the Culex species. These mosquitoes breed in stagnant water, such as swamps, marshes, and flooded areas. The virus circulates between mosquitoes and birds, with horses and humans serving as dead-end hosts. Infected mosquitoes can transmit the virus to humans through their bites.
The Life Cycle of the EEE Virus
The EEE virus has a complex life cycle that involves both birds and mosquitoes. Birds serve as the primary hosts, with the virus circulating in their bloodstream. When a mosquito bites an infected bird, it picks up the virus, which it can then transmit to other birds, humans, or horses. Environmental factors such as warm temperatures, high humidity, and abundant standing water can create ideal conditions for the virus to thrive, leading to increased risk of transmission.
Symptoms of EEE
EEE can cause a range of symptoms, depending on the severity of the infection. In mild cases, symptoms may include:
- Fever
- Headache
- Fatigue
- Chills
- Body aches
In severe cases, EEE can lead to:
- High fever
- Stiff neck
- Confusion
- Seizures
- Coma
- Death
It’s important to note that the symptoms of EEE can resemble those of other illnesses, such as meningitis or encephalitis. If you experience any of these symptoms, it’s crucial to seek medical attention immediately.
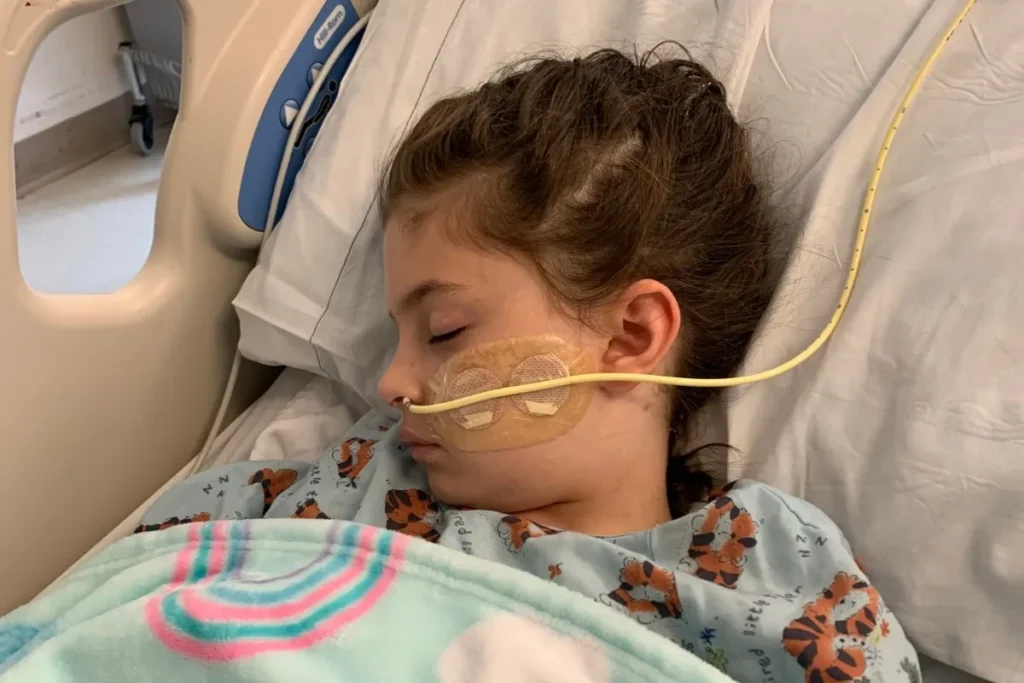
Personal Stories and Case Studies
The devastating impact of EEE is best understood through personal stories of those who have been affected. In 2019, a Massachusetts resident named Jim contracted EEE after a mosquito bite in his backyard. Within days, he was hospitalized with severe symptoms and later fell into a coma. Despite intensive medical care, Jim did not survive. His story is a somber reminder of the virus’s deadly potential and the importance of taking preventive measures seriously.
Risk Factors
Certain factors can increase your risk of contracting EEE:
- Age: Children under 15 and adults over 50 are at a higher risk.
- Location: Living in or visiting areas with high mosquito populations, such as rural or forested areas, increases your risk.
- Occupation: Individuals who work outdoors, such as farmers, landscapers, or agricultural workers, are at a greater risk.
- Immunosuppression: People with weakened immune systems are more susceptible to EEE.
Areas Affected in Massachusetts
EEE outbreaks in Massachusetts can occur in various regions, depending on factors like mosquito populations and weather conditions. It’s important to stay informed about the specific areas currently affected by the virus. You can find updates on the Massachusetts Department of Public Health website or through local news sources.
Precautions and Prevention
To protect yourself from EEE, it’s essential to take the following precautions:
- Avoid Mosquito Bites: Wear long-sleeved shirts, pants, and socks when outdoors, especially during dawn and dusk when mosquitoes are most active.
- Use Insect Repellent: Apply EPA-registered insect repellent containing DEET, picaridin, or other effective ingredients.
- Limit Outdoor Activities: Reduce your time outdoors during peak mosquito hours, especially in areas with standing water.
- Eliminate Standing Water: Mosquitoes breed in stagnant water, so eliminate any potential breeding grounds around your property, such as bird baths, flowerpots, or clogged gutters.
- Stay Informed: Monitor local news and health department updates for information on EEE outbreaks and prevention measures.
State Response and Public Health Initiatives
Massachusetts has taken proactive measures to combat EEE, particularly during active outbreak seasons. The state has implemented mosquito control programs that include spraying insecticides in high-risk areas, conducting public education campaigns, and monitoring mosquito populations. While these efforts have helped reduce the number of cases, the challenge of fully eradicating the virus remains.
Vaccination
While there is no vaccine specifically for EEE in humans, a vaccine is available for horses. Vaccinating horses can help prevent the spread of the virus and protect human health. Research is ongoing to develop a vaccine for humans, with scientists exploring various approaches to immunization.
Ongoing Research and Future Prevention
Researchers continue to study the EEE virus to better understand its transmission dynamics, improve diagnostic tools, and develop potential treatments. Advances in genetic analysis and vector control strategies offer hope for reducing the impact of EEE in the future. However, until a human vaccine is developed, public awareness and preventive measures remain the best defense against this deadly virus.
Seeking Medical Attention
If you experience symptoms consistent with EEE, it’s crucial to seek medical attention immediately. Early diagnosis and treatment can improve outcomes.
Conclusion
Eastern Equine Encephalitis is a serious public health threat in Massachusetts. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and prevention measures, you can take steps to protect yourself and your loved ones from this deadly virus. Stay informed about EEE outbreaks and follow the recommendations of local health authorities to minimize your risk.
for more information







